Sat, Jul 19, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 22, Issue 2 (JUNE 2025)
IJMSE 2025, 22(2): 169-181 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
dhifallah I, rhouma F, saafi I, bennaceur J, selmi W, dimessi W et al . Development of Branched ZnO Microrods: A Comprehensive Structural and Optical Characterization. IJMSE 2025; 22 (2) :169-181
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3884-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3884-en.html
Ines Dhifallah 
 , Faten Rhouma
, Faten Rhouma 
 , Imen Saafi
, Imen Saafi 
 , Jamila Bennaceur
, Jamila Bennaceur 
 , Wafa Selmi
, Wafa Selmi 
 , Wissem Dimessi
, Wissem Dimessi 
 , Radhouane Chtourou
, Radhouane Chtourou 


 , Faten Rhouma
, Faten Rhouma 
 , Imen Saafi
, Imen Saafi 
 , Jamila Bennaceur
, Jamila Bennaceur 
 , Wafa Selmi
, Wafa Selmi 
 , Wissem Dimessi
, Wissem Dimessi 
 , Radhouane Chtourou
, Radhouane Chtourou 

Abstract: (2835 Views)
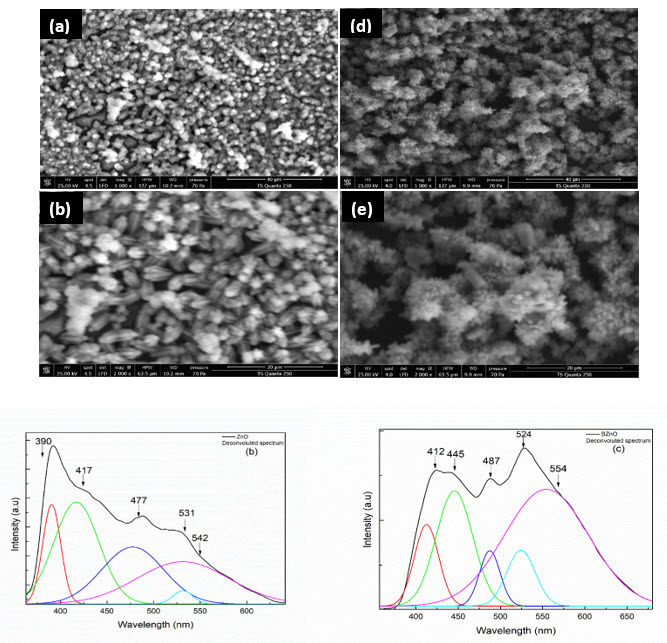
In this study, a novel three-step method for the synthesis of ZnO and branched ZnO microrods was developed. Numerous techniques were used to analyze the obtained samples: photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, raman spectroscopy, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-rays (EDX), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-visible) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The XRD study and Rietveld refinement confirmed that the synthesized samples have the hexagonal wurtzite structure of ZnO without any impurity with the P63mc space group. To further verify our experimental results, structural parameters were calculated by First Principles Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations and compared with experimental ones. A small decrease in the unit cell volume following the branching process was observed by the DFT calculations and Rietveld refinement results. Raman spectra showed peaks corresponding to the phonon modes of hexagonal wurtzite ZnO, which was consistent with the results of XRD and Rietveld refinement. SEM confirmed that ZnO and BZnO samples have hexagonal rod and branched rod shapes. BZnO showed stronger green PL emission but lower overall PL intensity compared to ZnO. The reduced photoluminescence (PL) intensity across all frequencies indicates enhanced separation of the photogenerated electron-hole pairs in branched ZnO (BZnO) due to decreased recombination.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Ceramic Materials and Engineering
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |