Tue, Jan 7, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 15, Issue 4 (December 2018)
IJMSE 2018, 15(4): 1-10 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Fallah Tafti M, Sedighi M, Hashemi R. Effects of Natural Aging Treatment on Mechanical, Microstructural and Forming Properties of Al 2024 Aluminum Alloy Sheets. IJMSE 2018; 15 (4) :1-10
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-1090-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-1090-en.html
Abstract: (19147 Views)
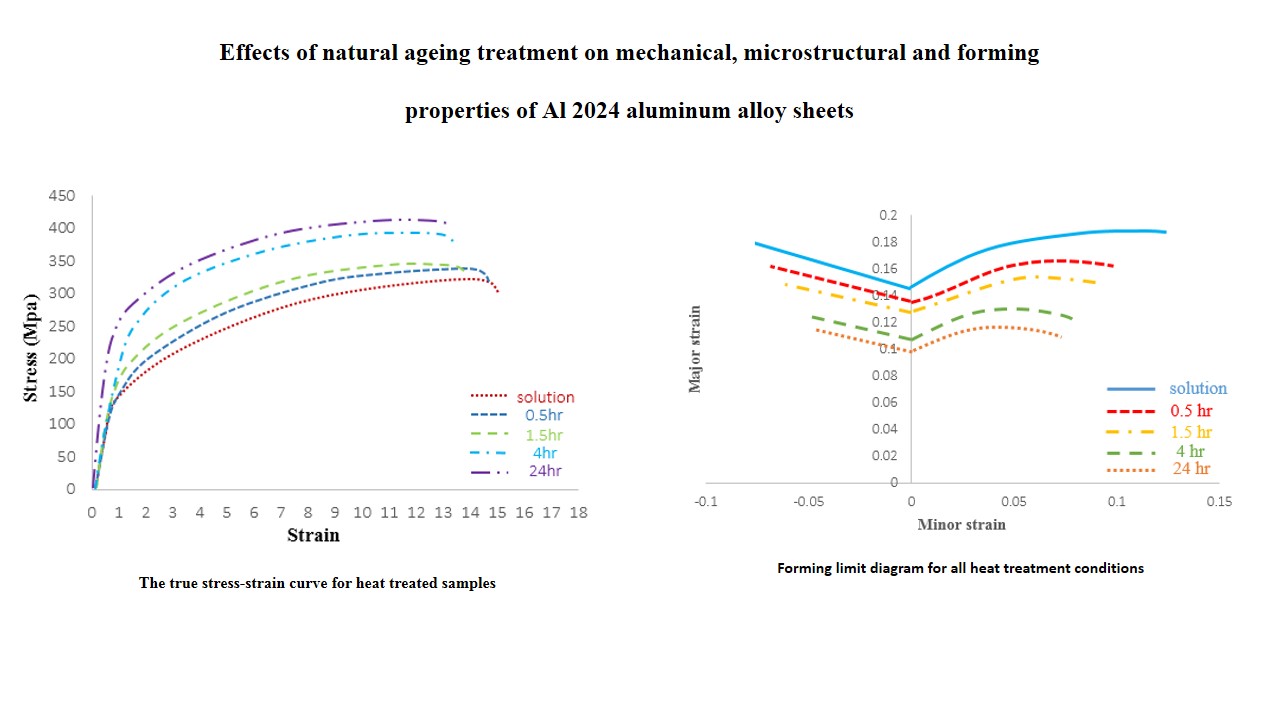
In this study, the microstructural variations, mechanical properties and forming limit diagrams (FLD) of Al 2024 aluminum alloy sheet with the thickness of 0.81mm are investigated during natural ageing (T4) treatment. The most formability in Al 2024 can be achieved just after solution treatment, and it is better to perform the forming process, on this aluminum alloy sheet, in this condition. However, in industrial applications, there is usually a postponement for some hours after solution treatment to begin the forming process that it means the forming process should be done at the natural ageing condition. This condition decreases the formability of Al 2024 sheets. To monitor the properties variations in natural ageing condition, FLDs are determined after specific times (e.g., 0.5, 1.5, 4 and 24 hours). The variations in micro-hardness, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and elongation at break are observed with changing the ageing time. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) investigations illustrated that density and size of precipitates are changed with ageing time. Moreover, the Nakazima test is utilized to study the forming limits considering the natural ageing condition. Results show by increasing the ageing time, up to 4hr, the majority of properties variations could be seen, and from 4hr to 24hr, the variations are changed slower.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
forming and mechanical properties
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |